I. Common stainless steel types and characteristics
304 stainless steel (food grade)
Composition: 18% chromium, 8% nickel (18/8 stainless steel), low carbon.
Advantages:
Strong corrosion resistance, acid and alkali resistance, oxidation resistance;
Meets food contact safety standards (FDA approved);
Good toughness, easy to process, no rust in long-term use.
Cons: Higher cost.
Applicable Scenarios:
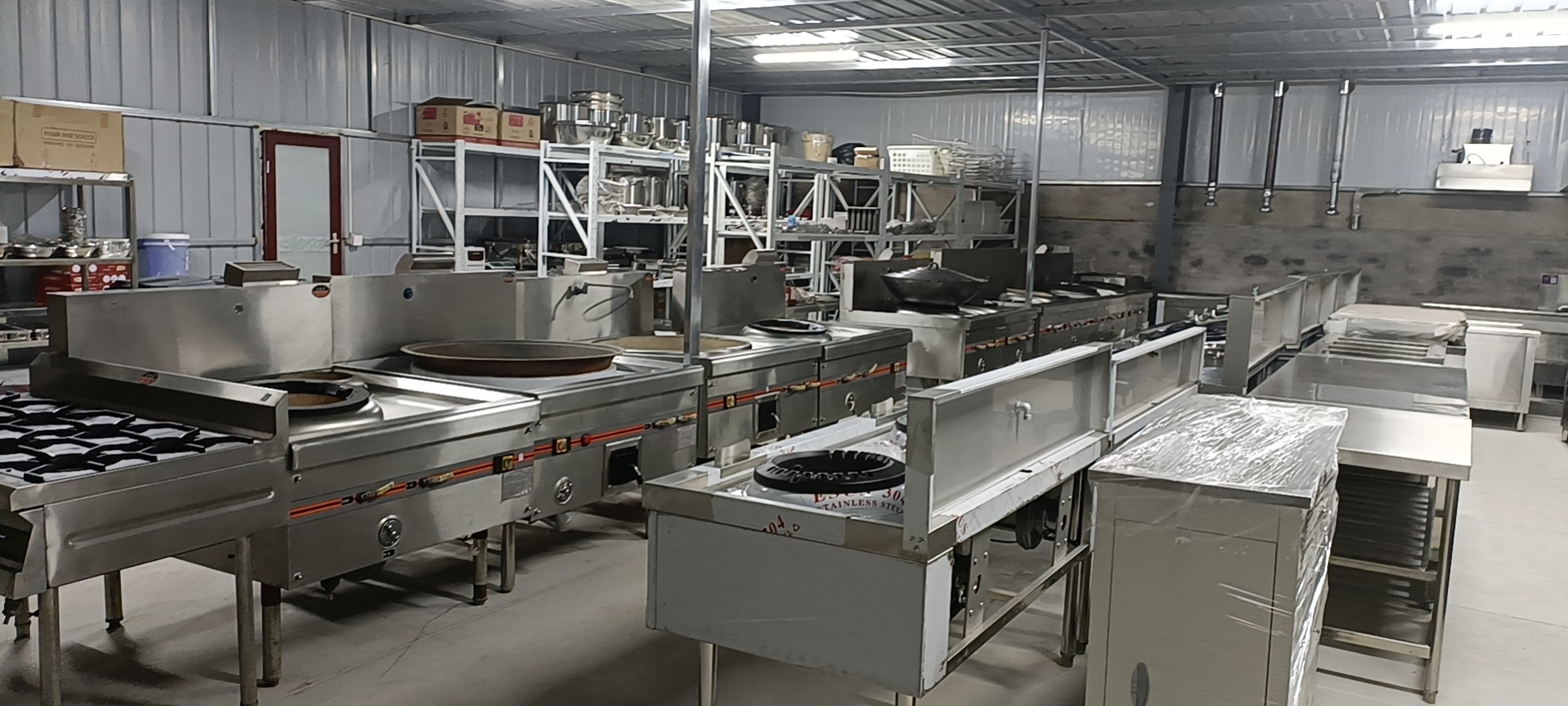
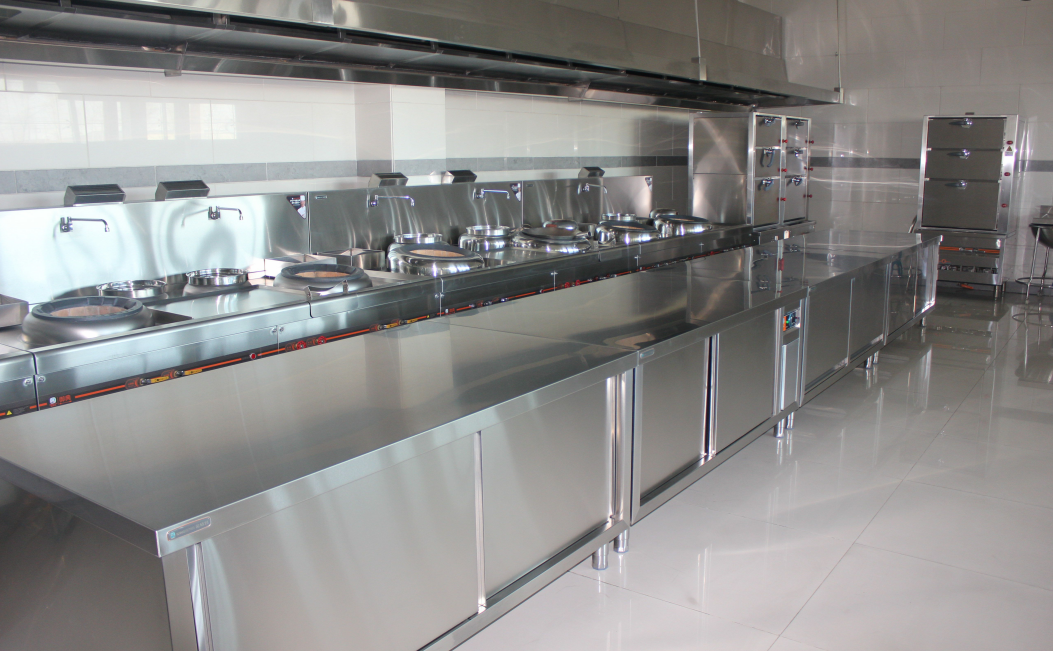
Parts in direct contact with ingredients (such as operating tables, sinks, pots and pans);
High temperature and high humidity environment (e.g. steam cabinet, sterilizer liner).
430 stainless steel (industrial grade)
Composition: 16%~18% chromium, nickel free.
Advantages:
Low cost, with certain anti-rust ability;
Stronger magnetism, suitable for parts with magnetic suction function.
Disadvantages:
Poor corrosion resistance, easy to rust with long-term contact with water or acid and alkali;
Lower hardness, easy to scratch.
Applicable Scenario:
Non-core components (such as cabinet shells, decorative panels) in dry environments;
Cost-sensitive kitchenware.
201 stainless steel (low-end alternative)
Composition: 16%~18% chromium, 3.5%~5.5% nickel (containing manganese to replace some of the nickel).
Advantages: low price, appearance close to 304.
Disadvantages:
Poor corrosion resistance, easy to rust (especially in humid or chlorine environment);
High manganese content, long-term contact with food may be a safety hazard.
Applicable scene:
Low-end kitchenware or temporary use equipment;
Structural parts in non-food contact areas (e.g. brackets, frames).
316 stainless steel (high-end corrosion resistance)
Composition: 16%~18% chromium, 10%~14% nickel, with 2%~3% molybdenum added.
Advantages:
Extremely corrosion resistant (especially resistant to chloride ion corrosion);
Suitable for harsh environments (e.g. coastal, frequent use of chemical cleaners).
Disadvantages: extremely high cost.
Scenario:
High-end commercial kitchen equipment (e.g. seawater treatment equipment, laboratory cookware);
Medical or special industrial environment.
II. Other factors affecting performance
Thickness (unit: mm)
Countertops, sinks and other load-bearing parts need to be ≥ 1.2mm, thin material is easy to deform;
Low-end products may use the following 0.8mm plate, short life.
Surface treatment process
Brushed: anti-scratch, easy to clean;
Mirror polishing: beautiful, but easy to leave fingerprints;
Sandblasting: increase friction, suitable for handle and other parts.
Welding process
High-quality products use argon arc welding, weld seam flat, corrosion-resistant;
Poor quality products spot welding or ordinary welding, easy to crack and rust.
Ⅲ, the purchase of recommendations
According to the use of selected materials:
Food contact area (such as cutting table, pots and pans) must choose 304 or 316;
Dry structural parts can choose 430 or 201 (need regular maintenance).
Identify the authenticity of the material:
Check the product label (e.g. “SUS304”);
Magnetic test: 304 micro-magnetism (may be magnetic after cold processing), 430 strong magnetism;
Chemical reagent test (such as manganese content test solution to distinguish 201 and 304).
Avoid the low price trap:
Below the market price of “304” kitchenware may be 201 counterfeit;
Requirements for material testing report (GB/T 3280 standard).
Translated with DeepL.com (free version)
If you need anything about commercial kitchen equipment, please feel free to contact us!
Learn more Commercial kitchen equipment
Commercial kitchenware|Commercial kitchen equipment|stainless steel|commercial oven|Oven|combi oven|combination stove|Dough proofer|commercial Western food kitchenware|Commercial refrigeration